# 代码来源:https://www.r2omics.cn/
# Mfuzz包的安装方式为:BiocManager::install("Mfuzz")
library(Mfuzz)
library(tidyverse)
library(patchwork)
# 先自定一个函数,之后直接调用
mfuzzHeatmap = function(data,
clusterNum=6
){
# data = df
# clusterNum=6
# 构建对象,填补缺失值,标准化等
dm <- data.matrix(data) # 数据框转换为矩阵
ESet <- new("ExpressionSet",exprs = dm) # 构建对象
ESet <- filter.NA(ESet, thres=0.25) # 过滤缺失值超过“25%”的基因
ESet <- fill.NA(ESet,mode="knn") # knn算法填补缺失值
ESet <- filter.std(ESet,min.std=0,visu=F)# 根据标准差去除样本间差异太小的基因
gene.s <- standardise(ESet) # 标准化
exprs(gene.s) # 查看处理后的数据
# 聚类
c <- clusterNum # 设置聚类个数
m <- mestimate(gene.s) # 评估出最佳的m值
set.seed(123) # 设置随机种子,防止每次聚类的结果都不一样,无法复现
cl <- mfuzz(gene.s, c = c, m = m)
cl # 查看每个基因聚到哪个类当中
cl$size # 查看每个cluster中的基因个数
cl$membership #查看基因和cluster之间的membership。如果两个基因对于一个特定的cluster都有高的membership score,那么他们通常来说表达模式是相似的
# ggplot2绘图
# 绘制趋势分析
dfMfuzz = exprs(gene.s) %>%data.frame()
dfMfuzz
dfColor = cl$membership %>%
data.frame(check.names = F) %>%
tibble::rownames_to_column("ID") %>%
pivot_longer(-1,names_to = "cluster",values_to = "Membership")
# 计算color的范围,让多张图的图例保持相同
colorLimit = dfColor %>%
group_by(ID) %>%
summarise(max=max(Membership,na.rm = T)) %>%
ungroup()
dfcluster = cl$cluster %>%
data.frame() %>%
set_names("Cluster") %>%
tibble::rownames_to_column("ID")
dfclusterSplit = dfcluster %>%
group_split(Cluster,.keep=T)
mfuzzPlotList = imap(dfclusterSplit,function(dataItem,i){
# dataItem = dfclusterSplit[[1]]
clusterName = dataItem$Cluster[[1]]
clusterID = dataItem %>% pull(ID)
myN = length(clusterID)
dfPlot = dfMfuzz[clusterID,] %>%
tibble::rownames_to_column("ID") %>%
pivot_longer(-1,names_to = "Sample",values_to = "Value") %>%
left_join(dfColor %>%
filter(cluster==clusterName)) %>%
arrange(Membership)
# dfPlot = dfPlot %>%
# filter(Membership>0.5)
p = ggplot(dfPlot,aes(x=Sample,y=Value,group=factor(ID,levels = unique(ID)),color=Membership))+
geom_line()+
scale_color_gradientn(colors =c("#5E4FA2","#3288BD","#66C2A5", # 设置渐变色
"#ABDDA4","#E6F598","#FFFFBF",
"#FEE08B", "#FDAE61","#F46D43",
"#D53E4F","#9E0142"),
breaks=seq(0,1,0.1),
limits=c(min(colorLimit$max,na.rm = T),max(colorLimit$max,na.rm = T))
)+
# scale_color_continuous(breaks=c(seq(0,1,0.1)),labels=c(seq(0,1,0.1)))+
theme_bw()+
labs(y=paste0("cluster ",clusterName,"\n","n=",myN),
x="")+
theme(legend.position = "top",
panel.grid.major=element_blank(),
panel.grid.minor=element_blank(),
axis.text.y = element_blank(),
axis.ticks.y = element_blank(),
plot.margin = unit(c(0, 0.1, 0, 0), "inches")
)+
scale_x_discrete(expand = c(0.05,0.05))
p
if(i==length(dfclusterSplit)){
}else{
p = p+
theme(axis.text.x = element_blank(), # 多张图是否只显示一个刻度
axis.ticks.x = element_blank(),
axis.title.x = element_blank())
}
p
})
# 绘制热图
heatmapList = imap(dfclusterSplit,function(dataItem,i){
# dataItem = dfclusterSplit[[1]]
clusterName = dataItem$Cluster[[1]]
clusterID = dataItem %>% pull(ID)
myN = length(clusterID)
dfMean.Zscore = t(data) %>%
scale() %>%
t() %>%
data.frame()
dfPlot = dfMean.Zscore[clusterID,] %>%
tibble::rownames_to_column("ID") %>%
pivot_longer(-1,names_to = "Sample",values_to = "Value")
dfPlot
p = ggplot(dfPlot,aes(x=Sample,y=ID,fill=Value))+
geom_tile()+
scale_fill_gradient2(low="#0000ff", high="#ff0000", mid="#ffffff",
breaks=seq(-3,3,0.5),
limits=c(min(dfMean.Zscore,na.rm = T),max(dfMean.Zscore,na.rm = T))
)+
theme_bw()+
labs(y="",x="",fill="Expression")+
theme(legend.position = "top",
panel.grid.major=element_blank(),
panel.grid.minor=element_blank(),
axis.text.y = element_blank(),
axis.ticks.y = element_blank(),
axis.title.y = element_blank(),
plot.margin = unit(c(0, 0, 0, 0), "inches")
)+
scale_x_discrete(expand = c(0,0))
if(i==length(dfclusterSplit)){
}else{
p = p+
theme(axis.text.x = element_blank(),
axis.ticks.x = element_blank(),
axis.title.x = element_blank(),)
}
p
})
# 合并
p = wrap_plots(c(mfuzzPlotList,heatmapList),byrow=F,ncol=2)+
plot_layout(guides = 'collect') & theme(legend.position='top')
return(
list(p=p,
dfcluster=dfcluster)
)
}R语言做趋势分析+热图
前言
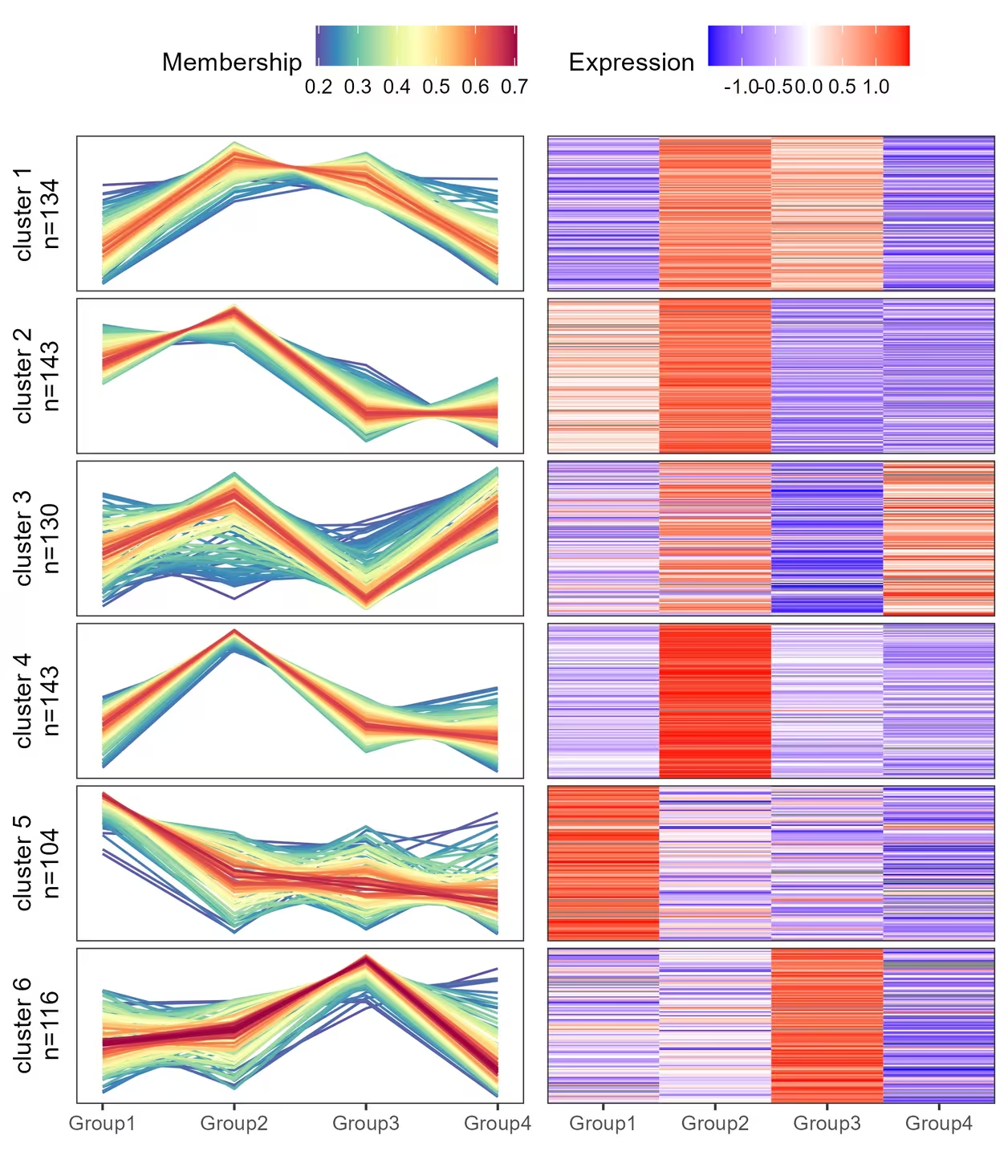
经常能在文献中看到趋势分析和热图的合并图,自己手搓了一个自定义函数,其实就是折线图和热图拼接起来。
绘图前的数据准备
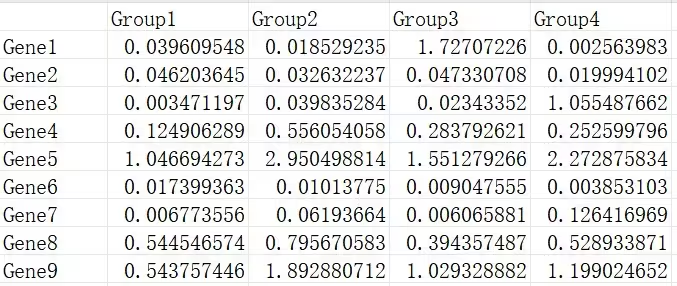
demo数据可以在https://www.r2omics.cn/res/demodata/mfuzz.xls下载。
数据包含2个维度,数据通常来源于搜库结果定量表,且需要有时序关系。一般都是用预处理后的数据,组内取平均值或中位数。
R语言怎么做
已提供示例数据,可直接运行。
可以直接用本篇提供的mfuzzHeatmap函数绘制趋势分析和热图的组合图,目前提供的可改参数只有聚类个数,其他细节修改可以直接修改函数对应的部分。
自定义函数 mfuzzHeatmap
调用自定义函数
# 代码来源:https://www.r2omics.cn/
# 读取时间序列分析数据文件
df = read.delim("https://www.r2omics.cn/res/demodata/mfuzz.xls",# 这里读取了网络上的demo数据,将此处换成你自己电脑里的文件
row.names = 1
)
result = mfuzzHeatmap(
data = df, # 数据
clusterNum = 6 # 聚类个数
)211 genes excluded.
0 genes excluded.# 绘图
result$p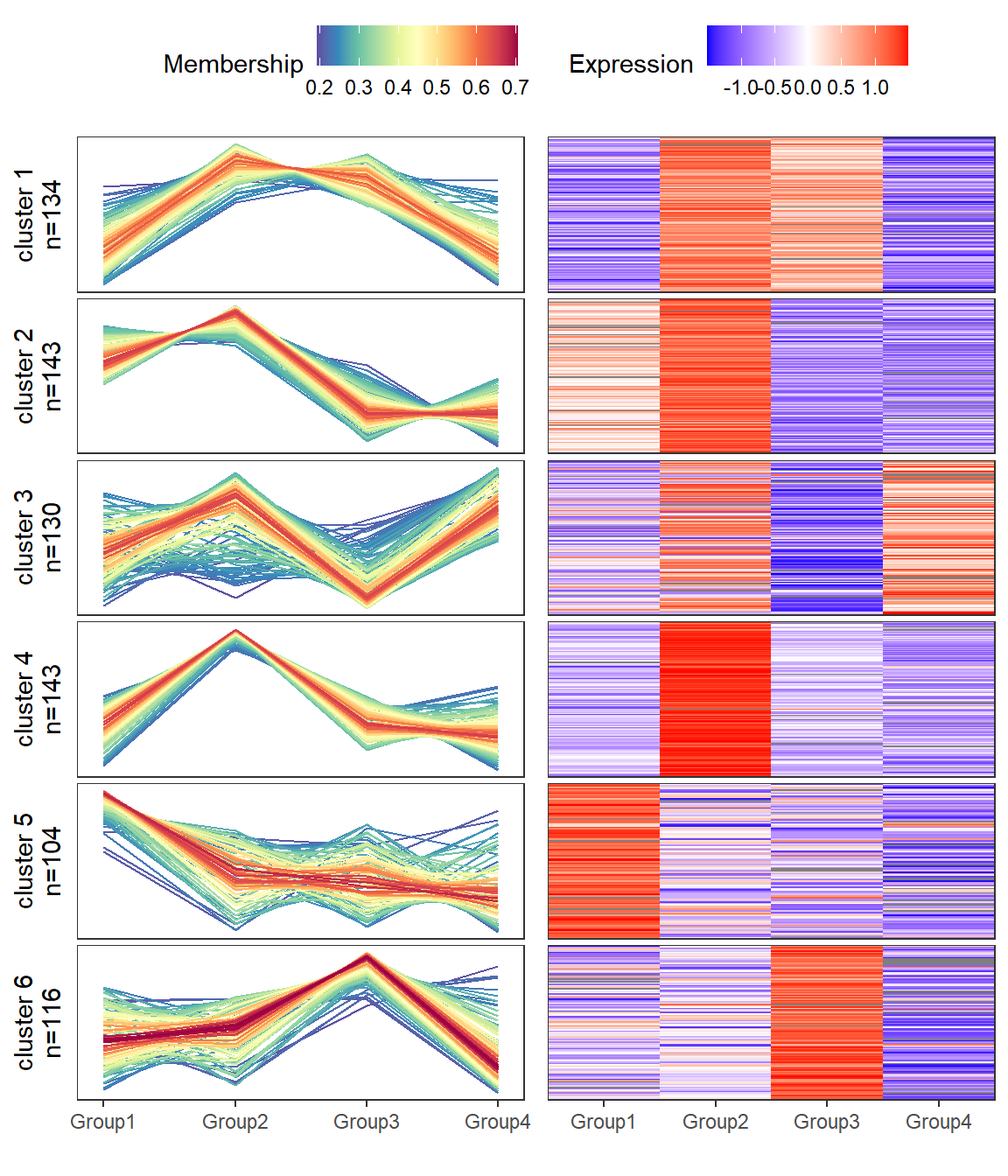
# 查看基因被聚到哪类中
head(result$dfcluster) ID Cluster
1 Gene1 5
2 Gene2 6
3 Gene4 4
4 Gene5 3
5 Gene8 2
6 Gene9 4