# A tibble: 150 × 5
Sepal.Length Sepal.Width Petal.Length Petal.Width Species
<dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <fct>
1 5.1 3.5 1.4 0.2 setosa
2 4.9 3 1.4 0.2 setosa
3 4.7 3.2 1.3 0.2 setosa
4 4.6 3.1 1.5 0.2 setosa
5 5 3.6 1.4 0.2 setosa
6 5.4 3.9 1.7 0.4 setosa
7 4.6 3.4 1.4 0.3 setosa
8 5 3.4 1.5 0.2 setosa
9 4.4 2.9 1.4 0.2 setosa
10 4.9 3.1 1.5 0.1 setosa
# ℹ 140 more rowsR语言如何绘制相关性矩阵
什么是相关性矩阵?
相关性是指两个或多个变量之间的关系或相互影响程度。若两组的值一起增大,我们称之为正相关,若一组的值增大时,另一组的值减小,我们称之为负相关。其值介于-1与1之间,即越接近1,越正相关;越接近-1,越负相关。
常见的有两种计算相关性的算法:皮尔逊相关性(pearson)和斯皮尔曼相关性(spearman)。皮尔逊相关性最常用,适合正态分布的数据。斯皮尔曼相关性是秩相关,不受极大极小值的影响。
在组学中的应用,例如,两个技术性重复实验的结果相关性很低,则说明数据有异常。
需要注意的地方,做样本之间的相关性的时候,蛋白之间要对应,不可随意打乱顺序。数据中有缺失值的情况,通常用”pairwise.complete.obs”算法处理缺失值,即两两配对删除缺失值。
计算完相关性后,我们通过相关性矩阵做可视化。矩阵的上下中多个个面板支持多种图案,有热力图,柱形图,散点图,折线图,饼图等多种模式可供选择。
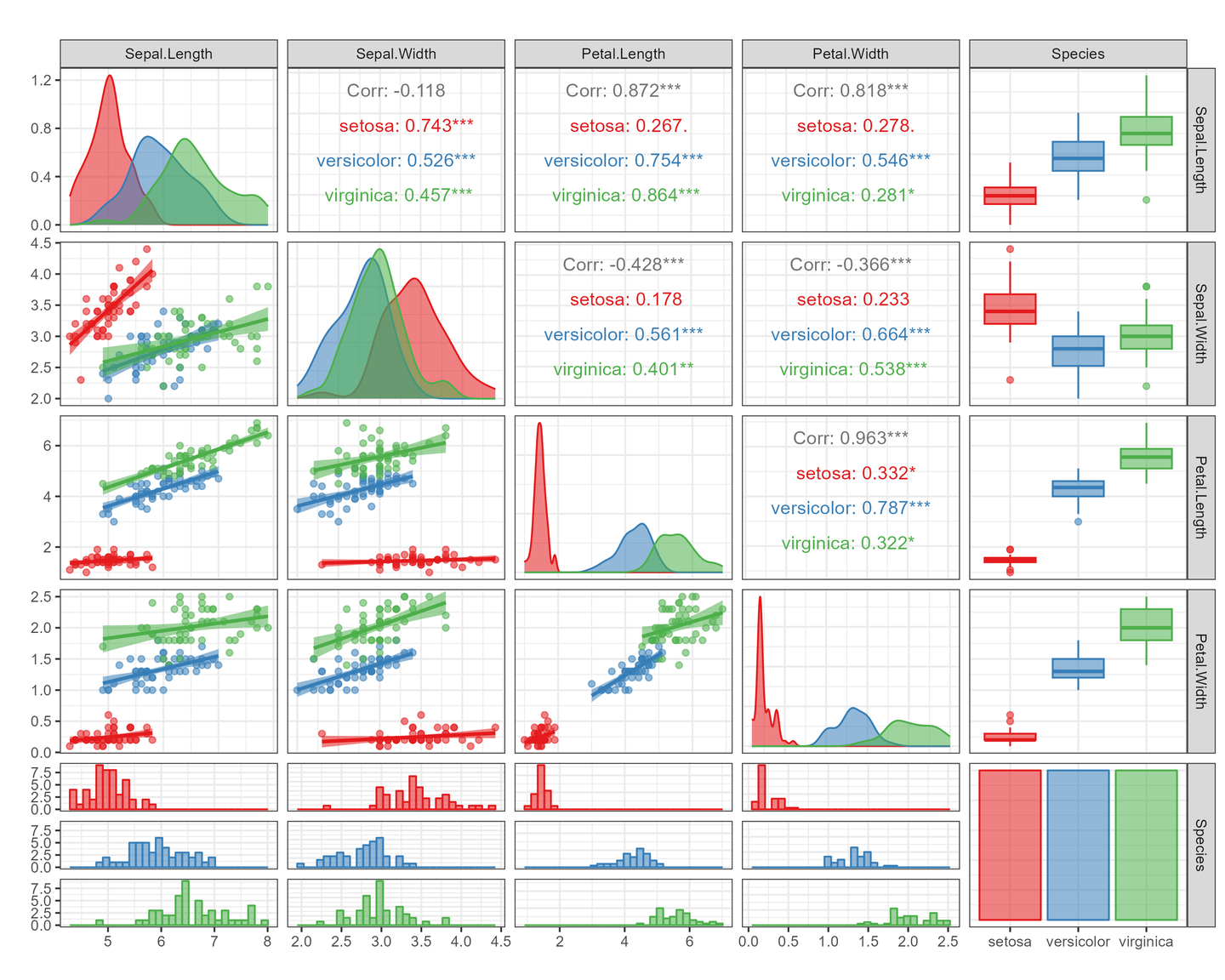
绘图前的数据准备
这里就用R语言自带的示例数据了,iris
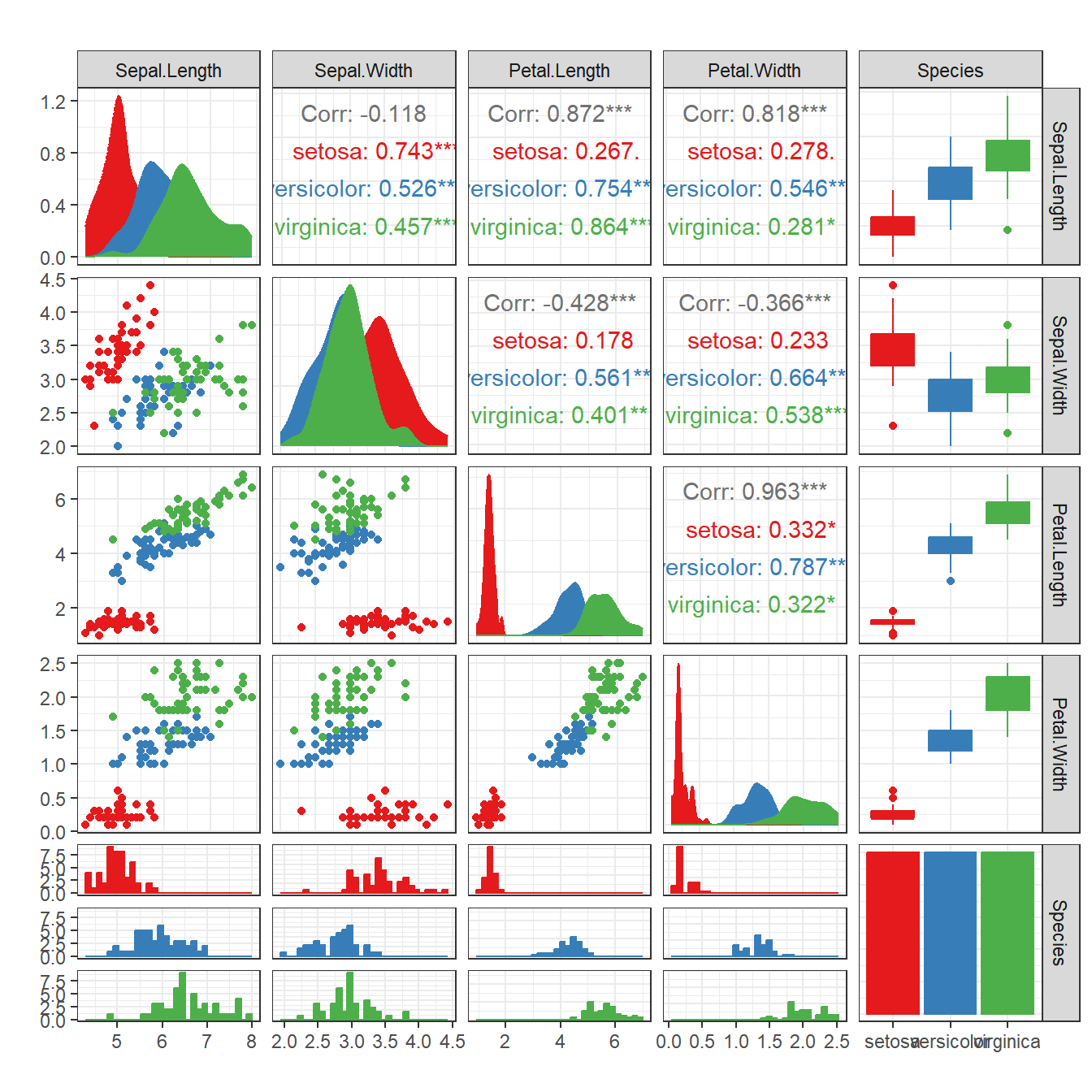
R语言如何绘制相关性矩阵图
本篇是用R包GGally做相关性矩阵图的教程
# 代码来源:https://www.r2omics.cn/
library(GGally)
# 绘图
ggpairs(
data = iris, # 数据
mapping = aes(fill = Species, color = Species), # 映射,同ggplot2
# columns = 1:ncol(data), # 对选中的列绘图,默认是全部列
upper = list( # 指定上方面板,各种情况下的使用的图形,有哪些参数见下方附录
continuous = "cor", # xy轴都是连续型向量时的图案
combo = "box_no_facet", # xy轴有一个时候连续型,另一个是离散型时的图案
discrete = "count", # xy轴都是离散型向量时的图案
na = "blank" # 当某个方向的数据全为NA时,显示的内容
),
lower = list( # 指定下方面板,各种情况下的使用的图形
continuous = "points",
combo = "facethist",
discrete = "facetbar",
na = "na"
),
diag = list( # 指定中间面板,各种情况下的使用的图形
continuous = "densityDiag",
discrete = "barDiag",
na = "naDiag"
),
axisLabels = "show", # 轴标签的显示方式,内部显示:internal 不显示:none
# columnLabels = c("a", "b", "c", "d", "e"), # 分面标签显示的名称,默认为列名
switch = NULL, # 分面标签的位置,x:右下, y:左上, both:左下, NULL:右上
showStrips = NULL # NULL:只显示右上方的分页标签 True:显示所有矩阵中的分页标签
)+
# ggpairs底层基于ggplot2, 可以用其他的ggplot2语法修改,例如
theme_bw()+ # 主题
scale_fill_manual(values = c("#e41a1c", "#377eb8", "#4daf4a", "#984ea3")) + # fill调色
scale_color_manual(values = c("#e41a1c", "#377eb8", "#4daf4a", "#984ea3"))+ # color调色
labs( # 坐标轴名称选项
x = "", # x轴名称
y = "", # y轴名称
title = "" # 标题名字
)
附录:
该包提供的上下中面板中的形状有很多,可以在https://ggobi.github.io/ggally/articles/ggally_plots.html参考
上下面板
continuous:xy轴都是连续型向量时的图案
cor:相关性数字
density:二维密度图
points:散点图
smooth, smooth_lm, smooth_loess:带回归线的散点图
discrete: xy轴都是离散型向量时的图案
colbar:百分比簇状图
autopoint
count cross crosstable :tile 系列
facetbar
ratio
rowbar

table
trends
combo: xy轴有一个时候连续型,另一个是离散型时的图案
autopoint
box box_no_facet
denstrip
dot dot_no_facet
facetdensitystrip
facethist
summarise_by
trends
na: 当某个方向的数据全为NA时,显示的内容
blank
na
中间面板
continuous
‘densityDiag’, ‘barDiag’, ‘blankDiag’
discrete
‘barDiag’, ‘blankDiag’
na
‘naDiag’, ‘blankDiag’